How to Set Up a Chessboard: A Step-by-Step Guide
 How to set Up a Chess Board – A Step-by-Step Guide
How to set Up a Chess Board – A Step-by-Step Guide
Chess is a timeless game of strategy, intellect, and skill. But before you can dive into a thrilling match, you need to set up the chessboard correctly. Whether you’re a beginner or just need a refresher, this guide will walk you through the proper setup so you can start playing right away.
- The chess board is made up of a total of 64 equally sized squares of white and dark color. These squares are alternately white and dark.
- In the game of chess, two players play against each other by placing the pieces in a board. When placing this board, the white square in the corner of the board should be in the player’s right hand.
Headline Ideas:
- How to Set Up a Chess Board Correctly (Every Time!)
- Beginner’s Guide: Setting Up a Chess Board Like a Pro
- Don’t Get It Backwards! Learn the Right Way to Set Up a Chess Board
- Start with a brief hook: Emphasize how a correct setup is the first step to playing chess properly.
- Mention that many beginners unknowingly make mistakes, and this guide is here to prevent that.
- Highlight that this article is perfect for kids, parents, teachers, or anyone new to chess.
 Section 1: Understanding the Chess Board
Section 1: Understanding the Chess Board
The initial position of the chess board
- The board has 64 squares (8 rows × 8 columns), alternating light and dark colors.
- Tip: “Light on right” – the square in the bottom-right corner should always be a light square.
- The bottom-right square (from White’s perspective) must always be a light square – this helps you orient the board correctly.
- Ensure the board is positioned so that each player has a white (or light-colored) square on their bottom-right corner.
 Symmetry and Balance
Symmetry and Balance
The chessboard is symmetrical, meaning both players have equal access to all files, ranks, and diagonals. This ensures fairness and balance, where strategy and skill — not board position — determine the outcome.
✅ Incorrect Chess Board Setup (for illustration)
- A flipped board or pieces on wrong squares (like queen and king swapped)
🖼️ Caption idea: “Common mistake: Board is set up incorrectly. Watch the square colors and piece order.”
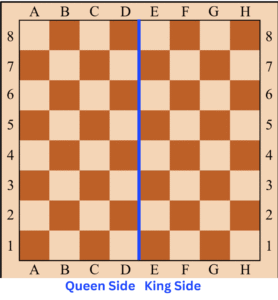
🔶 Introduction Queen Side and King Side
- Begin with a hook:
“Ever wondered why some players say ‘castle kingside’ or ‘attack on the queenside’? These are not just fancy terms — they define critical regions of the board!” - Introduce the concept: The chessboard is split into two logical halves — the kingside and the queenside — and understanding this division is essential for planning, attacking, and castling.
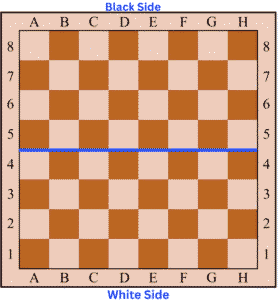
🔶 Introduction White Side and Black Side
In chess, the board is divided into two sides — the White side and the Black side — each controlled by one player.
- The player sitting behind the white pieces is said to have the White side, and the one sitting behind the black pieces has the Black side.
- One of the most important rules in chess is that White always moves first.
🔶 Center Squares – The Heart of the Board
The four center squares — d4, d5, e4, and e5 — are considered the most important in the opening phase of the game. Controlling these central squares allows your pieces more mobility and strategic power.
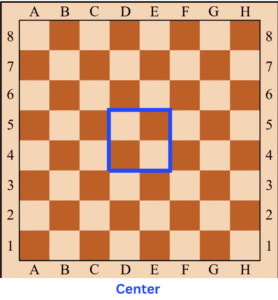
On a standard 8×8 chessboard, The four center squares — d4, d5, e4, and e5. These squares form a small square right in the middle of the board and are often referred to as the “classical center.”
There are also extended center squares, which include the eight surrounding squares:
- c3, c4, c5, c6
- d3, d6
- e3, e6
- f3, f4, f5, f6
 Understanding Ranks and Files on a Chessboard
Understanding Ranks and Files on a Chessboard
When learning chess, one of the first concepts to understand is how the board is labeled. The chessboard is made up of 64 squares arranged in 8 rows and 8 columns, and each square has a unique name based on its file and rank.
 What Are Ranks and Files?
What Are Ranks and Files?
- Ranks are the horizontal rows numbered from 1 to 8 (bottom to top from White’s side).
- Files are the vertical columns labeled from a to h (left to right from White’s side).
✅ Ranks = horizontal rows = 1 to 8 (bottom to top from White’s view)
✅ Files = vertical columns = a to h (left to right from White’s view)


- The squares that are of the same color and touch each other at the corners are called pentagonal diagonals.
- There are a total of 26 such diagonals on the board, 13 white and 13 dark colors.
 The names of the squares on the chessboard :
The names of the squares on the chessboard :
- Each square on the board has a unique name by which that square is identified.
- Each square is made up of the letters of the files and the rank numbers.
This is very easy to understand.
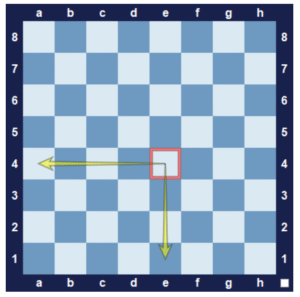
Let’s see how to identify the name of a square on a board with an example.
First, look at the files of that square and then look at the rank of that square.
The file of the square shown in the above figure is e and the rank of that square is 4, then the name of that square is e4.
 Practical Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
Practical Exercise: Test Your Knowledge
- What is the notation for the square where the White king starts?
Answer: e1
2. If a pawn moves from e2 to e4, how is it written in notation
Answer: e4

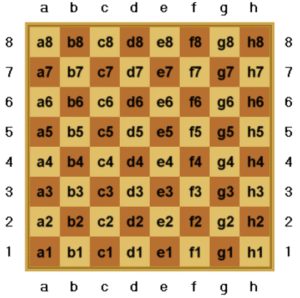
 Section 2: Placing the Pieces – Step by Step
Section 2: Placing the Pieces – Step by Step
Break this down clearly and logically: Explain how this -Names of all the squares on the chessboard
 Step 1: Correct Chess Board Setup (Initial Position)
Step 1: Correct Chess Board Setup (Initial Position)
- Full board with pieces in their starting positions
- Light square at bottom right

 Chess Pieces
Chess Pieces
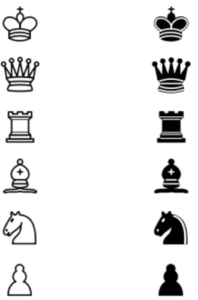
King ⇒ K
Queen ⇒ Q
Rook ⇒ R
Bishop ⇒ B
Knight ⇒ N
Pawn ⇒ P
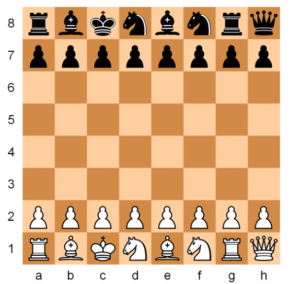
Explain how this orientation is critical. Incorrect orientation leads to wrong placement of pieces.
 Step 2: Arrange the Pawns
Step 2: Arrange the Pawns
- Each player has 8 pawns, which form the front line.
- Place them on the second row (rank) for White and the seventh row for Black.
- White pawns on row 2 (a2 to h2), Black pawns on row 7 (a7 to h7)
 Step 3: Set Up the Rooks (Castles)
Step 3: Set Up the Rooks (Castles)
- The rooks go in the corners of the board.
- For White, place them on a1 and h1.
- For Black, place them on a8 and h8.
 Step 4: Position the Knights (Horses)
Step 4: Position the Knights (Horses)
- The knights stand next to the rooks.
- White knights go on b1 and g1.
- Black knights go on b8 and g8.
 Step 5: Place the Bishops
Step 5: Place the Bishops
- The bishops go beside the knights.
- White bishops are on c1 and f1.
- Black bishops are on c8 and f8.
 Step 6: Add the Queen (The Most Powerful Piece)
Step 6: Add the Queen (The Most Powerful Piece)
- The queenalways starts on her matching color:
- White queen on d1 (a white square).
- Black queen on d8 (a black square).
- Remember: “Queen gets her color.”
- Place the queen on her own color
 Step 7: Place the King (The Most Important Piece)
Step 7: Place the King (The Most Important Piece)
- The king takes the remaining square next to the queen.
- White king on e1.
- Black king on e8.
 Standard Chess Board & Piece Size -Everything You Need to Know
Standard Chess Board & Piece Size -Everything You Need to Know
Whether you’re setting up a chess preparing for a school tournament, or curious about what makes a chess set “tournament standard,” it’s important to know the correct sizes of the chess board and pieces. Let’s dive into the official sizes used in tournaments and what you should look for when buying a chess set.
If you’re preparing to organize a FIDE-rated chess tournament or about the official standards for tournament play, understanding the proper chess board and piece sizes is essential.
Adhering to FIDE’s specifications ensures a fair and professional playing environment. Whether you’re organizing a scholastic event, a club tournament, or an international championship, choosing the right board and pieces helps enhance the experience for players and arbiters alike.
FIDE (World Chess Federation) provides clear guidelines to ensure uniformity and clarity during competitive play. Here’s everything you need to know:
1. Recommended Chess Board Dimensions
 Square Size:
Square Size:
- FIDE Standard: 5 cm to 6 cm per square (2–2.36 inches).
- USCF Standard: 2 to 2.5 inches per square (5.08–6.35 cm).
 Total Board Size:
Total Board Size:
- Square Size: 5.0 to 6.0 cm (approximately 2.0 to 2.5 inches)
- Full Board Size: Around 40 cm to 50 cm per side (16 to 20 inches), depending on square size
- Orientation: Light-colored square must be on the bottom-right corner
Tip: The square should be about 1.25 to 1.3 times the base diameter of the king for proper proportion.
FIDE suggests the square size should be about 1.25 to 1.3 times the base diameter of the king.
 Material & Design:
Material & Design:
- Non-reflective matte finish (wood or vinyl preferred).
- Contrasting colors (e.g., white/cream vs. dark brown/green/black).
- Board Type -Wood, vinyl, or plastic (matte finish)
2. Chess Piece Sizes (FIDE & USCF Standards)
 King Height (Most Important Measurement):
King Height (Most Important Measurement):
- FIDE: 8.5 cm to 10.5 cm (3.35–4.13 in).
- USCF: 3.375 to 4.5 inches (8.57–11.43 cm).
 Ideal King-to-Square Ratio
Ideal King-to-Square Ratio
To ensure balance and ease of play:
- The base of the king should be 75–80% of the square size.
- For a king with a 40 mm base, the square should ideally be 50 mm (5 cm).
Tip: The square should be about 1.25 to 1.3 times the base diameter of the king for proper proportion.
 Recommended Piece Sizes:
Recommended Piece Sizes:
| Chess Piece | Height (mm) | Ideal Base Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| King | 85–105 mm | 38–42 mm |
| Queen | 75–90 mm | Proportional |
| Bishop | 70–80 mm | Proportional |
| Knight | 65–75 mm | Proportional |
| Rook | 50–60 mm | Proportional |
| Pawn | 40–50 mm | Proportional |
 Key Requirements:
Key Requirements:



- Light and dark contrasting squares (e.g., black vs. white, buff & brown, white & green not similar shades).
- No bright or reflective colors.
3. How to Choose the Right Set for Tournaments
 For FIDE Events:
For FIDE Events:
- Board: 5–6 cm squares, non-reflective.
- Pieces: King height 9–10 cm, Staunton style.
 For USCF Events:
For USCF Events:
- Board: 2–2.5 inch squares.
- Pieces: King height 3.75–4.5 inches.
 Common Mistakes to Avoid:
Common Mistakes to Avoid:



4. Additional Tournament Equipment
Chess Clock: Digital (DGT 3000, ZMart, etc.) for FIDE events.
 Popular Tournament Sets
Popular Tournament Sets
Many tournaments use:
- Staunton-style pieces (FIDE-approved).
- Vinyl roll-up boards with 55 mm squares for practicality.
- Weighted pieces to prevent tipping during fast games.
